The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA),[1][2] informally referred to as Obamacare,[3][4] is a United States federal statute signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. The law (along with the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010) is the principal health care reform legislation of the 111th United States Congress. PPACA requires individuals not covered by employer- or government-sponsored insurance plans to maintain minimal essential health insurance coverage or pay a penalty unless exempted for religious beliefs or financial hardship, a provision commonly referred to as the individual mandate. The Act also reforms certain aspects of the private health insurance industry and public health insurance programs, increases insurance coverage of pre-existing conditions, expands access to insurance to 30 million Americans,[5][6] and increases projected national medical spending while reducing the national deficit, slowing health care cost inflation,[7][8] and lowering projected Medicare spending.[9]
PPACA passed the Senate on December 24, 2009, by a vote of 60–39 with all Democrats and two Independents voting for, and all but one Republican voting against.[10] It passed the House of Representatives on March 21, 2010, by a vote of 219–212, with 34 Democrats and all 178 Republicans voting against the bill.[11]
A majority of the states, and numerous organizations and individual persons, filed actions in federal court challenging the constitutionality of some or all of the elements of PPACA.[12] On June 28, 2012, in the case of National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius, the Supreme Court upheld the majority of the law, ruling that the mandate was a tax and therefore fell under Congress' taxing authority. The court, however, prevented the federal government from withholding allMedicaid funds to states that fail to comply with the expansion of Medicaid,[13][14][15][16] but rather only permitted the federal government to withhold new Medicaid funding from noncompliant states.[17]
[edit]Overview
PPACA includes numerous provisions to take effect over several years beginning in 2010. Policies issued before the law was promulgated aregrandfathered from most federal regulations.
- Guaranteed issue and partial community rating will require insurers to offer the same premium to all applicants of the same age and geographical location without regard to most pre-existing conditions (excluding tobacco use).[19][20][21]
- A shared responsibility requirement, commonly called an individual mandate,[22][23] requires that all persons not covered by an employer sponsored health plan, Medicaid, Medicare or other public insurance programs, purchase and comply with an approved private insurance policy or pay a penalty, unless the applicable individual is a member of a recognized religious sect exempted by the Internal Revenue Service, or waived in cases of financial hardship.[24]
- Medicaid eligibility is expanded to include all individuals and families with incomes up to 133% of the poverty level along with a simplifiedCHIP enrollment process.[25][26]
- Health insurance exchanges will commence operation in each state, offering a marketplace where individuals and small businesses can compare policies and premiums, and buy insurance (with a government subsidy if eligible).[27]
- Low income persons and families above the Medicaid level and up to 400% of the federal poverty level will receive federal subsidies[28] on a sliding scale if they choose to purchase insurance via an exchange (persons at 150% of the poverty level would be subsidized such that their premium cost would be of 2% of income or $50 a month for a family of 4).[29]
- Minimum standards for health insurance policies are to be established and annual and lifetime coverage caps will be banned.[30][31][32]
- Firms employing 50 or more people but not offering health insurance will also pay a shared responsibility requirement if the government has had to subsidize an employee's health care.[33]
- Very small businesses will be able to get subsidies if they purchase insurance through an exchange.[34]
- Co-payments, co-insurance, and deductibles are to be eliminated for select health care insurance benefits considered to be part of an "essential benefits package"[35] for Level A or Level B preventive care.[36][37]
- Changes are enacted that allow a restructuring of Medicare reimbursement from "fee-for-service" to "bundled payments."[38][39]
- Additional support is provided for medical research and the National Institutes of Health.[40]
[edit]Summary of funding
The Act's provisions are intended to be funded by a variety of taxes and offsets. Major sources of new revenue include a much-broadened Medicare tax on incomes over $200,000 and $250,000, for individual and joint filers respectively, an annual fee on insurance providers, and a 40% tax on "Cadillac" insurance policies. There are also taxes on pharmaceuticals, high-cost diagnostic equipment, and a 10% federal sales tax on indoor tanning services. Offsets are from intended cost savings such as improved fairness in the Medicare Advantage program relative to traditional Medicare.[41]
Summary of tax increases:
- Broaden Medicare tax base for high-income taxpayers: $210.2 billion
- Annual fee on health insurance providers: $60 billion
- 40% excise tax on health coverage in excess of $10,200/$27,500: $32 billion
- Impose annual fee on manufacturers and importers of branded drugs: $27 billion
- Impose 2.3% excise tax on manufacturers and importers of certain medical devices: $20 billion
- Raise 7.5% Adjusted Gross Income floor on medical expenses deduction to 10%: $15.2 billion
- Limit contributions to flexible spending arrangements in cafeteria plans to $2,500: $13 billion
- All other revenue sources: $14.9 billion
- Original budget estimates included a provision to require information reporting on payments to corporations, which had been projected to raise $17 billion, but the provision was repealed.[42]
[edit]Provisions
The Act is divided into 10 titles[43] and contains provisions that became effective immediately, 90 days after enactment, and six months after enactment, as well as provisions that will become effective in 2014.[44][45]
Below are some of the key provisions of the Act. For simplicity, the amendments in the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 are integrated into this timeline.[46][47]
[edit]Effective at enactment
- The Food and Drug Administration is now authorized to approve generic versions of biologic drugs and grant biologics manufacturers 12 years of exclusive use before generics can be developed.[48]
- The Medicaid drug rebate for brand name drugs is increased to 23.1% (except the rebate for clotting factors and drugs approved exclusively for pediatric use increases to 17.1%), and the rebate is extended to Medicaid managed care plans; the Medicaid rebate for non-innovator, multiple source drugs is increased to 13% of average manufacturer price.[48]
- A non-profit Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute is established, independent from government, to undertake comparative effectiveness research.[48] This is charged with examining the "relative health outcomes, clinical effectiveness, and appropriateness" of different medical treatments by evaluating existing studies and conducting its own. Its 19-member board is to include patients, doctors, hospitals, drug makers, device manufacturers, insurers, payers, government officials and health experts. It will not have the power to mandate or even endorse coverage rules or reimbursement for any particular treatment. Medicare may take the Institute's research into account when deciding what procedures it will cover, so long as the new research is not the sole justification and the agency allows for public input.[49] The bill forbids the Institute to develop or employ "a dollars per quality adjusted life year" (or similar measure that discounts the value of a life because of an individual's disability) as a threshold to establish what type of health care is cost effective or recommended. This makes it different from the UK's National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence.
- Creation of task forces on Preventive Services and Community Preventive Services to develop, update, and disseminate evidenced-based recommendations on the use of clinical and community prevention services.[48]
- The Indian Health Care Improvement Act is reauthorized and amended.[48]
- Chain restaurants and food vendors with 20 or more locations are required to display the caloric content of their foods on menus, drive-through menus, and vending machines. Additional information, such as saturated fat, carbohydrate, and sodium content, must also be made available upon request.[50] But first, the Food and Drug Administration has to come up with regulations, and as a result, calories disclosures may not appear until 2013 or 2014.[50]
[edit]Effective June 21, 2010
- Adults with existing conditions became eligible to join a temporary high-risk pool, which will be superseded by the health care exchange in 2014.[45][51] To qualify for coverage, applicants must have a pre-existing health condition and have been uninsured for at least the past six months.[52] There is no age requirement.[52] The new program sets premiums as if for a standard population and not for a population with a higher health risk. Allows premiums to vary by age (4:1), geographic area, and family composition. Limit out-of-pocket spending to $5,950 for individuals and $11,900 for families, excluding premiums.[52][53][54]
[edit]Effective July 1, 2010
- The President established, within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), a council to be known as the National Prevention, Health Promotion and Public Health Council to help begin to develop a National Prevention and Health Promotion Strategy. The Surgeon General shall serve as the Chairperson of the new Council.[55][56]
- A 10% tax on indoor tanning took effect.[57]
[edit]Effective September 23, 2010
- Insurers are prohibited from imposing lifetime dollar limits on essential benefits, like hospital stays, in new policies issued.[58]
- Dependents (children) will be permitted to remain on their parents' insurance plan until their 26th birthday,[59] and regulations implemented under the Act include dependents that no longer live with their parents, are not a dependent on a parent's tax return, are no longer a student, or are married.[60][61]
- Insurers are prohibited from excluding pre-existing medical conditions (except in grandfathered individual health insurance plans) for children under the age of 19.[62][63]
- Insurers are prohibited from charging co-payments, co-insurance, or deductibles for Level A or Level B preventive care and medical screenings on all new insurance plans.[64]
- Individuals affected by the Medicare Part D coverage gap will receive a $250 rebate, and 50% of the gap will be eliminated in 2011.[65] The gap will be eliminated by 2020.
- Insurers' abilities to enforce annual spending caps will be restricted, and completely prohibited by 2014.[45]
- Insurers are prohibited from dropping policyholders when they get sick.[45]
- Insurers are required to reveal details about administrative and executive expenditures.[45]
- Insurers are required to implement an appeals process for coverage determination and claims on all new plans.[45]
- Enhanced methods of fraud detection are implemented.[45]
- Medicare is expanded to small, rural hospitals and facilities.[45]
- Medicare patients with chronic illnesses must be monitored/evaluated on a 3 month basis for coverage of the medications for treatment of such illnesses.
- Companies which provide early retiree benefits for individuals aged 55–64 are eligible to participate in a temporary program which reduces premium costs.[45]
- A new website installed by the Secretary of Health and Human Services will provide consumer insurance information for individuals and small businesses in all states.[45]
- A temporary credit program is established to encourage private investment in new therapies for disease treatment and prevention.[45]
[edit]Effective January 1, 2011
- Insurers must spend a certain percent of premium dollars on eligible expenses, subject to various waivers and exemptions; if an insurer fails to meet this requirement, there is no penalty, but a rebate must be issued to the policy holder.[66][67][68]
- The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services is responsible for developing the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation and overseeing the testing of innovative payment and delivery models.[69]
- Flexible spending accounts, Health reimbursement accounts and health savings accounts cannot be used to pay for over-the-counter drugs, purchased without a prescription, except insulin.[70]
[edit]Effective January 1, 2012
- Employers must disclose the value of the benefits they provided beginning in 2012 for each employee's health insurance coverage on the employees' annual Form W-2's.[71]This requirement was originally to be effective January 1, 2011, but was postponed by IRS Notice 2010-69 on October 23, 2010.[72]
- New tax reporting changes were to come in effect to prevent tax evasion by corporations. However, in April 2011, Congress passed and President Obama signed the Comprehensive 1099 Taxpayer Protection and Repayment of Exchange Subsidy Overpayments Act of 2011 repealing this provision, because it was burdensome to small businesses.[73][74] Before PPACA businesses were required to notify the IRS on form 1099 of certain payments to individuals for certain services or property over a reporting threshold of $600.[75][76] Under the repealed law, reporting of payments to corporations would also be required.[77][78] Originally it was expected to raise $17 billion over 10 years.[79] The amendments made by Section 9006 of the Act were designed to apply to payments made by businesses after December 31, 2011, but will no longer apply because of the repeal of the section.[74][76]
[edit]Effective by August 1, 2012
- All new plans must cover certain preventive services such as mammograms and colonoscopies without charging a deductible, co-pay or coinsurance. Women's Preventive Services – including well-woman visits, support for breastfeeding equipment, contraception and domestic violence screening – will be covered without cost sharing.
[edit]Effective by January 1, 2013
- Income from self-employment and wages of single individuals in excess of $200,000 annually will be subject to an additional tax of 0.9%. The threshold amount is $250,000 for a married couple filing jointly (threshold applies to joint compensation of the two spouses), or $125,000 for a married person filing separately.[80] In addition, an additional tax of 3.8% will apply to the lesser of net investment income or the amount by which adjusted gross income exceeds $200,000 ($250,000 for a married couple filing jointly; $125,000 for a married person filing separately.)[81]
[edit]Effective by January 1, 2014
- Insurers are prohibited from discriminating against or charging higher rates for any individuals based on pre-existing medical conditions.[82]
- Impose an annual tax of $95, or up to 1% of income, whichever is greater, on individuals who do not secure insurance; this will rise to $695, or 2.5% of income, by 2016. This is an individual limit; families have a limit of $2,085.[24][83] Exemptions to the tax in cases of financial hardship or religious beliefs are permitted.[24] On June 28, 2012, the Supreme Court ruled that this penalty "must be construed as imposing a tax on those who do not have health insurance." According to the Supreme Court, Congress does not have the power under the Commerce Clause to levy a penalty for remaining uninsured. However, Congress does have the power to levy a tax in this instance.
- Insurers are prohibited from establishing annual spending caps.[45]
- Expand Medicaid eligibility; all individuals with income up to 133% of the poverty line qualify for coverage, including adults without dependent children.[24][84]
- Two years of tax credits will be offered to qualified small businesses. In order to receive the full benefit of a 50% premium subsidy, the small business must have an average payroll per full-time equivalent ("FTE") employee, excluding the owner of the business, of less than $25,000 and have fewer than 11 FTEs. The subsidy is reduced by 6.7% per additional employee and 4% per additional $1,000 of average compensation. As an example, a 16 FTE firm with a $35,000 average salary would be entitled to a 10% premium subsidy.[85]
- Impose a $2,000 per employee tax penalty on employers with more than 50 employees who do not offer health insurance to their full-time workers (as amended by the reconciliation bill).[86]
- Set a maximum of $2,000 annual deductible for a plan covering a single individual or $4,000 annual deductible for any other plan (see 111HR3590ENR, section 1302). These limits can be increased under rules set in section 1302.
- The CLASS Act provision would have created a voluntary long-term care insurance program, but in October 2011 the Department of Health and Human Services announced that the provision was unworkable and would be dropped, although an Obama administration official later said the President does not support repealing this provision.[87][88][89][90]
- Pay for new spending, in part, through spending and coverage cuts in Medicare Advantage, slowing the growth of Medicare provider payments (in part through the creation of a new Independent Payment Advisory Board), reducing Medicare and Medicaid drug reimbursement rate, cutting other Medicare and Medicaid spending.[47][91]
- Revenue increases from a new $2,500 limit on tax-free contributions to flexible spending accounts (FSAs), which allow for payment of health costs.[92]
- Establish health insurance exchanges, and subsidization of insurance premiums for individuals in households with income up to 400% of the poverty line. To qualify for the subsidy, the beneficiaries cannot be eligible for other acceptable coverage.[93][84][94][95] Section 1401(36B) of PPACA explains that the subsidy will be provided as an advanceable, refundable tax credit[96] and gives a formula for its calculation.[97] Refundable tax credit is a way to provide government benefit to people even with no tax liability[98] (example: Earned Income Credit). The formula was changed in the amendments (HR 4872) passed March 23, 2010, in section 1001. According to DHHS and CRS, in 2014 the income-based premium caps for a "silver" healthcare plan for family of four would be the following:
| Income % of federal poverty level | Premium Cap as a Share of Income | Income $ (family of 4)a | Max Annual Out-of-Pocket Premium | Premium Savingsb | Additional Cost-Sharing Subsidy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 133% | 3% of income | $31,900 | $992 | $10,345 | $5,040 |
| 150% | 4% of income | $33,075 | $1,323 | $9,918 | $5,040 |
| 200% | 6.3% of income | $44,100 | $2,778 | $8,366 | $4,000 |
| 250% | 8.05% of income | $55,125 | $4,438 | $6,597 | $1,930 |
| 300% | 9.5% of income | $66,150 | $6,284 | $4,628 | $1,480 |
| 350% | 9.5% of income | $77,175 | $7,332 | $3,512 | $1,480 |
| 400% | 9.5% of income | $88,200 | $8,379 | $2,395 | $1,480 |
a.^ Note: In 2016, the FPL is projected to equal about $11,800 for a single person and about $24,000 for family of four.[103][104] See Subsidy Calculator for specific dollar amount.[105]
b.^ DHHS and CBO estimate the average annual premium cost in 2014 to be $11,328 for family of 4 without the reform.[99]
b.^ DHHS and CBO estimate the average annual premium cost in 2014 to be $11,328 for family of 4 without the reform.[99]
- The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) and Internal Revenue Service (IRS) on August 12, 2011, issued joint proposed rules regarding implementation of new state-based health insurance exchanges to cover how the exchanges will determine eligibility for uninsured individuals and employees of small businesses seeking to buy insurance on the exchanges, as well as how the exchanges will handle eligibility determinations for low-income individuals applying for newly expanded Medicaid benefits.[102][106][107][108]
- Members of Congress and their staff will only be offered health care plans through the exchange or plans otherwise established by the bill (instead of the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program that they currently use).[109]
- A new excise tax goes into effect that is applicable to pharmaceutical companies and is based on the market share of the company; it is expected to create $2.5 billion in annual revenue.[83]
- Most medical devices become subject to a 2.3% excise tax collected at the time of purchase. (Reduced by the reconciliation act to 2.3% from 2.6%)[110]
- Health insurance companies become subject to a new excise tax based on their market share; the rate gradually raises between 2014 and 2018 and thereafter increases at the rate of inflation. The tax is expected to yield up to $14.3 billion in annual revenue.[83]
- The qualifying medical expenses deduction for Schedule A tax filings increases from 7.5% to 10% of earned income.[111]
[edit]Effective by January 1, 2015
- Physicians' payments from federally funded programs such as Medicare will be modified to be based on the quality of care, not the volume.
[edit]Effective by January 1, 2017
- A state may apply to the Secretary of Health & Human Services for a "waiver for state innovation" provided that the state passes legislation implementing an alternative health care plan meeting certain criteria. The decision of whether to grant the waiver is up to the Secretary (who must annually report to Congress on the waiver process) after a public comment period.[112]
- A state receiving the waiver would be exempt from some of the central requirements of the ACA, including the individual mandate, the creation by the state of an insurance exchange, and the penalty for certain employers not providing coverage.[113][114] The state would also receive compensation equal to the aggregate amount of any federal subsidies and tax credits for which its residents and employers would have been eligible under the ACA plan, but which cannot be paid out due to the structure of the state plan.[112]
- In order to qualify for the waiver, the state plan must provide insurance at least as comprehensive and as affordable as that required by the ACA, must cover at least as many residents as the ACA plan would, and cannot increase the federal deficit. The coverage must continue to meet the consumer protection requirements of the ACA, such as the prohibition on increasing premiums because of pre-existing conditions.[115]
- A bipartisan bill sponsored by Senators Ron Wyden and Scott Brown, and supported by President Obama, proposes making waivers available in 2014 rather than 2017, so that, for example, states that wish to implement an alternative plan need not set up an insurance exchange only to dismantle it a short time later.[113]
- Vermont has announced its intention to pursue a waiver in order to implement the single-payer system enacted in May 2011.[116][117][118][119] Oregon is also expected to request a waiver.[120]
[edit]Effective by 2018
- All existing health insurance plans must cover approved preventive care and checkups without co-payment.[45]
- A new 40% excise tax on high cost ("Cadillac") insurance plans is introduced. The tax (as amended by the reconciliation bill)[121] is on the cost of coverage in excess of $27,500 (family coverage) and $10,200 (individual coverage), and it is increased to $30,950 (family) and $11,850 (individual) for retirees and employees in high risk professions. The dollar thresholds are indexed with inflation; employers with higher costs on account of the age or gender demographics of their employees may value their coverage using the age and gender demographics of a national risk pool.[83][122]
[edit]Effective by 2020
- The Medicare Part D coverage gap (aka "donut hole") would be completely phased out and hence closed.
[edit]Legislative history
[edit]Background
Main articles: Health care reform in the United States, Health care reform debate in the United States, and Health care reforms proposed during the Obama administration
Health care reform was a major topic of discussion during the 2008 Democratic presidential primaries. As the race narrowed, attention focused on the plans presented by the two leading candidates, New York Senator Hillary Clinton and the eventual nominee, Illinois Senator Barack Obama. Each candidate proposed a plan to cover the approximately 45 million Americans estimated to be without health insurance at some point during each year. One point of difference between the plans was that Clinton's plan was to require all Americans to obtain coverage (in effect, an individual health insurance mandate), while Obama's was to provide a subsidy but not create a direct requirement.
During the general election campaign between Obama and the Republican nominee, Arizona Senator John McCain, Obama said that fixing health care would be one of his four priorities if he won the presidency.[123] After his inauguration, Obama announced to a joint session of Congress in February 2009 that he would begin working with Congress to construct a plan for health care reform.[124] On March 5, 2009, Obama formally began the reform process and held a conference with industry leaders to discuss reform and requested reform be enacted before the Congressional summer recess; but the reform was not passed by the requested date.[125] In July 2009, a series of bills were approved by committees within the House of Representatives.[126] Beginning June 17, 2009, and extending through September 14, 2009, three Democratic and three Republican Senate Finance Committee Members met for a series of 31 meetings to discuss the development of a health care reform bill. Over the course of the next three months, this group, Senators Max Baucus (D-Montana), Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), Kent Conrad (D-North Dakota), Olympia Snowe (R-Maine), Jeff Bingaman (D-New Mexico), and Mike Enzi (R-Wyoming), met for more than 60 hours, and the principles that they discussed became the foundation of the Senate's health care reform bill.[127] The meetings were held in public and broadcast by C-SPAN and can be seen on the C-SPAN web site[128] or at the Committee's own web site.[129] During the August 2009 congressional recess, many members went back to their districts and entertained town hall meetings to solicit public opinion on the proposals. During the summer recess, the Tea Party movement organized protests and manyconservative groups and individuals targeted congressional town hall meetings to voice their opposition to the proposed reform bills.[125][130]
Away from the televised meetings, the legislation became a "bonanza" for lobbyists,[131][132] including secret deals that were initially denied but subsequently confirmed.[133][134]The Sunlight Foundation documented many of the reported ties between "the healthcare lobbyist complex" and politicians in both major parties.[135]
President Obama delivered a speech to a joint session of Congress supporting reform and again outlining his proposals.[136][137] On November 7, the House of Representatives passed the Affordable Health Care for America Act on a 220–215 vote and forwarded it to the Senate for passage.[125][138]
The Senate bill, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, bore similarities to prior healthcare reform proposals introduced by Republicans. In 1993 Senator John Chafeeintroduced the Health Equity and Access Reform Today Act which contained a "Universal Coverage" requirement with a tax penalty for non-compliance.[139][140] In 1994 SenatorDon Nickles introduced the Consumer Choice Health Security Act which also contained an individual mandate with a penalty provision.[141] However, Nickles removed the mandate from the act shortly after introduction, stating that they had decided "that government should not compel people to buy health insurance."[142]
There were many threats made against members of Congress and many were assigned extra protection.[143][144][145][146][147][148][148][149][150][151][143][152][147][153][154][155][156][157][158][159]
[edit]Senate
The Senate failed to take up debate on the House bill and instead took up H.R. 3590, a bill regarding housing tax breaks for service members.[160] As the United States Constitution requires all revenue-related bills to originate in the House,[161] the Senate took up this bill since it was first passed by the House as a revenue-related modification to the Internal Revenue Code. The bill was then used as the Senate's vehicle for their health care reform proposal, completely revising the content of the bill.[162] The bill as amended incorporated elements of earlier proposals that had been reported favorably by the Senate Health and Finance committees.
Passage in the Senate was temporarily blocked by a filibuster threat by Nebraska Senator Ben Nelson, who sided with the Republican minority. Nelson's support for the bill was won after it was amended to offer a higher rate of Medicaidreimbursement for Nebraska.[125] The compromise was derisively referred to as the "Cornhusker Kickback"[163] (and was later repealed by the reconciliation bill). On December 23, the Senate voted 60–39 to end debate on the bill, eliminating the possibility of a filibuster by opponents. The bill then passed by a party-line vote of 60–39 on December 24, 2009, with one senator (Jim Bunning) not voting.[164]
On January 19, 2010, Massachusetts Republican Scott Brown was elected to the Senate, having campaigned on giving the Republican minority the 41st vote needed to sustain a filibuster, even famously signing autographs as "Scott 41."[125][165][166]
[edit]House
Although White House Chief of Staff Rahm Emanuel argued for a less ambitious bill, House Speaker Nancy Pelosi pushed back, dismissing Emanuel's scaled-down approach as "Kiddie Care".[167][168] Obama's siding with comprehensive reform and the news that Anthem Blue Cross in California intended to raise premium rates for its patients by as much as 39% gave him a new line of argument for reform.[167][168] Obama unveiled a health care reform plan of his own, drawing largely from the Senate bill. On February 22 he laid out a "Senate-leaning" proposal to consolidate the bills.[169] On February 25, he held a meeting with leaders of both parties urging passage of a reform bill.[125] The summit proved successful in shifting the political narrative away from the Massachusetts loss back to health care policy.[168]
The most viable option for the proponents of comprehensive reform was for the House to abandon its own health reform bill, the Affordable Health Care for America Act, and to instead pass the Senate's bill, and then pass amendments to it with a different bill allowing the Senate to pass the amendments via the reconciliation process.[167][170]
Initially, there were not enough supporters to pass the bill, thus requiring its proponents to negotiate with a group of pro-lifeDemocrats, led by Congressman Bart Stupak. The group found the possibility of federal funding for abortion was substantive enough to cause their opposition to the bill. Instead of requesting inclusion of additional language specific to their abortion concerns in the bill, President Obama issued Executive Order 13535, reaffirming the principles in the Hyde Amendment. This concession won the support of Stupak and members of his group and assured passage of the bill.[171]
The House passed the bill with a vote of 219 to 212 on March 21, 2010, with 34 Democrats and all 178 Republicans voting against it.[172] The following day, Republicans introduced legislation to repeal the bill.[173] Obama signed the original bill into law on March 23, 2010.[174]
[edit]Impact
[edit]Public policy impact
[edit]Federal expenditures and deficit impact
See also: United States public debt
[edit]Expenditure estimates
In 2012, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projected the Act will require more than $1.7 trillion in gross federal spending over the period 2012-2022, some of which will be offset by penalties and tax increases related to coverage, resulting in net spending of more than $1.2 trillion.[175][176][177][178]
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, by 2019 the Act will increase expenditures on Medicaid and individual subsidies by $165 billion annually while reducing Medicare expenditures by $125 billion annually.[179]
[edit]CBO deficit reduction estimates
The 2011 comprehensive CBO estimate projected a net deficit reduction of more than $200 billion during the period 2012-2021.[180] CBO estimated in March 2011 that for the 2012-2021 period, the law would result in net receipts of $813 billion, offset by $604 billion in outlays, resulting in a $210 billion reduction in the deficit.[180]
As of the bill's passage into law in 2010, CBO estimated the legislation would reduce the deficit by $143 billion[181] over the first decade, but half of that was due to expected premiums for the C.L.A.S.S. Act, which has since been abandoned.[182]Although the CBO generally does not provide cost estimates beyond the 10-year budget projection period (because of the great degree of uncertainty involved in the data) it decided to do so in this case at the request of lawmakers, and estimated a second decade deficit reduction of $1.2 trillion.[183][184] CBO predicted deficit reduction around a broad range of one-half percent of GDP over the 2020s while cautioning that "a wide range of changes could occur".[185]
CBO also initially stated that the bill would "substantially reduce the growth of Medicare's payment rates for most services; impose an excise tax on insurance plans with relatively high premiums; and make various other changes to the federal tax code, Medicare, Medicaid, and other programs;"[183] A commonly heard criticism of the CBO cost estimates is that CBO was required to exclude from its initial estimates the effects of likely "doc fix" legislation that would increase Medicare payments by more than $200 billion from 2010 to 2019;[186][187][188][189][190] however, the "doc fix" remains a separate piece of legislation.[191] Subject to the same exclusion, the CBO initially estimated the federal government's share of the cost during the first decade at $940 billion, $923 billion of which takes place during the final six years (2014–2019) when the spending kicks in;[192][193] with revenue exceeding spending during these six years.[194]
[edit]Controversy over "double-counting" Medicare savings
There is a controversy regarding whether Medicare program savings are "double-counted" when they are reported as both reducing the deficit and improving the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance (HI) Fund. CBO estimated in December 2009 that PPACA would increase Medicare HI revenues by $113 billion while reducing Medicare Part A (HI-related) outlays by $245 billion during the 2010-2019 period, a roughly $400 billion increase (including interest) in the HI Fund. This extends the date of HI Fund exhaustion by several years. Further, since the government is spending less and taking in more, it also reduces the deficit.[195]
However, because Medicare program surpluses are spent on other government programs and must ultimately be paid back to Medicare recipients, an increase in the HI Fund is in fact an obligation of the government, part of the "intragovernmental debt" that along with the "debt held by the public" add up to the "public debt" or "national debt" commonly reported in the media. This will require funding from other sources once the Medicare program goes into deficit. This is how government trust fund accounting has traditionally been done and PPACA did not diverge from this practice. The Social Security Trust Fund is handled similarly. CBO wrote: "Trust fund accounting shows the magnitude of the savings within the trust fund, and those savings indeed improve the solvency of that fund; however, that accounting ignores the burden that would be faced by the rest of the government later in redeeming the bonds held by the trust fund."[195][196]
CBO and Medicare actuaries acknowledge that budget rules required them to double-count Medicare reductions even though in practice they "cannot be simultaneously used to finance other federal outlays (such as the coverage expansions) and to extend the [Medicare] trust fund, despite the appearance of this result from the respective accounting conventions."[197] According to the Washington Post, "in 2010 the CBO wrote that, absent the Medicare savings, the law would increase deficits by $226 billion through 2019 — instead of decreasing them by the commonly cited $132 billion."[198] Charles Blahous, public trustee overseeing Medicare and Social Security finances, projected in 2012 that PPACA would add more than $300 billion to the deficit over the next decade.[199][200]
The issue generated considerable debate outside government.[201] Paul Krugman called the Blahous study "bogus,"[202] and the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities (CBPP), anon-profit think tank, published a dismissal of the "double counting canard" as inconsistent with historical deficit computation practices, pointing out that "the Medicare actuary says that health reform will extend the solvency of the Hospital Insurance trust fund by eight years."[203] Blahous answered with a rebuttal, noting all sides agreed that his study reflected "current law."[204] Forbes published a summary calling the debate "a battle over baselines," with one side being "the literal reading of current law" and the other projecting "current practice forward."[205] Analyzing the Medicare trustees' 2012 annual report, Forbes presented the two views: either (1) the Medicare Hospital Insurance trust fund remains solvent through 2016, but the CBO scores the ACA as deficit neutral; or (2) the trust fund remains solvent through 2024, "and Blahous’ score of the ACA as increasing the deficit by $300-500 billion is accurate."[206]
[edit]
There was mixed opinion about the CBO estimates from others.
Uwe Reinhardt, a health economist at Princeton, wrote that "The rigid, artificial rules under which the Congressional Budget Office must score proposed legislation unfortunately cannot produce the best unbiased forecasts of the likely fiscal impact of any legislation", but went on to say "But even if the budget office errs significantly in its conclusion that the bill would actually help reduce the future federal deficit, I doubt that the financing of this bill will be anywhere near as fiscally irresponsible as was the financing of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003."[207]
Douglas Holtz-Eakin, a former CBO director who served during the George W. Bush administration, opined that the bill would increase the deficit by $562 billion.[208]
Republican House leadership and the Republican majority on the House Budget Committee estimate the law would increase the deficit by more than $700 billion in its first 10 years.[209][210]
Democratic House leadership and the Democratic minority on the House Budget Committee say the claims of budget gimmickry are false[211] and that repeal of the legislation would increase the deficit by $230 billion over the same period,[212] pointing to the CBO's 2011 analysis of the impact of repeal.[213]
The New Republic editors Noam Scheiber (an economist) and Jonathan Cohn (a noted health care policy analyst), countered critical assessments of the law's deficit impact, arguing that it is as likely, if not more so, for predictions to have underestimated deficit reduction than to have overestimated it. They noted that it is easier, for example, to account for the cost of definite levels of subsidies to specified numbers of people than account for savings from preventive health care, and that the CBO has a track record of consistently overestimating the costs of, and underestimating the savings of health legislation;[214][215] "innovations in the delivery of medical care, like greater use of electronic medical records and financial incentives for more coordination of care among doctors, would produce substantial savings while also slowing the relentless climb of medical expenses... But the CBO would not consider such savings in its calculations, because the innovations hadn't really been tried on such large scale or in concert with one another--and that meant there wasn't much hard data to prove the savings would materialize."[215]
David Walker, former U.S. Comptroller General now working for The Peter G. Peterson Foundation, has stated that the CBO estimates are not likely to be accurate, because it is based on the assumption that Congress is going to do everything they say they're going to do.[216] On the other hand, a Center on Budget and Policy Priorities analysis said that Congress has a good record of implementing Medicare savings. According to their study, Congress implemented the vast majority of the provisions enacted in the past 20 years to produce Medicare savings.[217][218]
[edit]Healthcare spending trends
In a May 2010 presentation on "Health Costs and the Federal Budget", CBO stated:
- Rising health costs will put tremendous pressure on the federal budget during the next few decades and beyond. In CBO's judgment, the health legislation enacted earlier this year does not substantially diminish that pressure.
CBO further observed that "a substantial share of current spending on health care contributes little if anything to people's health" and concluded, "Putting the federal budget on a sustainable path would almost certainly require a significant reduction in the growth of federal health spending relative to current law (including this year's health legislation)."[219]
[edit]Change in number of uninsured
CBO estimates the legislation will reduce the number of uninsured residents by 30 million, leaving 25 million uninsured residents in 2019 after the bill's provisions have all taken effect.[220][221][178][176] Among the people in this uninsured group will be:
- Illegal immigrants, estimated at almost a third of the 25 million---they will be ineligible for insurance subsidies and Medicaid;[220][222][223] they will also be exempt from thehealth insurance mandate and will remain eligible for emergency services under the 1986 Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA).
- Citizens not enrolled in Medicaid despite being eligible.[224]
- Citizens not otherwise covered and opting to pay the annual penalty instead of purchasing insurance---mostly younger and single Americans.[224]
- Citizens whose insurance coverage would cost more than 8% of household income and are exempt from paying the annual penalty.[224]
Early experience under the Act was that, as a result of the tax credit for small businesses, many of them offered health insurance to their employees for the first time.[225]
On September 13, 2011, the Census Bureau released a report showing that the number of uninsured 19- to 25-year-olds (now eligible to stay on their parents' policies) had declined by 393,000, or 1.6%, both statistically significant.[226]
[edit]Coverage for abortifacients, contraceptives, and sterilizations
Main article: Contraceptive mandates
With the exception of churches and houses of worship, the Act's contraceptive coverage mandate applies to all employers and educational institutions. The mandate applies to all new health insurance plans effective August 2012. It controversially includes Christian hospitals, Christian charities, Catholic universities, and other enterprises owned or controlled by religious organizations that oppose contraception on moral grounds. Regulations[227] made under the act rely on the recommendations of the Institute of Medicine, which concluded that birth control is medically necessary "to ensure women's health and well-being."
In February 2012, a major political controversy erupted with candidates for the Republican nomination for President viewing the regulations as a "direct attack on religious liberty".[228] However, certain aspects of the mandate are not new. In December 2000, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission ruled that companies that provided prescription drugs to their employees but didn't provide birth control were in violation of Title VII of the 1964 Civil Rights Act, which prevents discrimination on the basis of sex. That opinion, which the George W. Bush administration did nothing to alter or withdraw when it took office the next month, is still in effect today—and because it relies on Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, it applies to all employers with 15 or more employees. Currently, employers that don't offer prescription coverage or don't offer insurance at all are exempt, because they treat men and women equal, but the new mandate will penalize such actions.
After the EEOC opinion was approved in 2000, reproductive rights groups and employees who wanted birth control access sued employers that refused to comply. The next year, in Erickson v. Bartell Drug Co., a federal court agreed with the EEOC's reasoning. Reproductive rights groups and others used that decision as leverage to force other companies to settle lawsuits and agree to change their insurance plans to include birth control. Some subsequent court decisions echoed Erickson, and some went the other way, but the rule (absent a Supreme Court decision) remained, and over the following decade, the percentage of employer-based plans offering contraceptive coverage tripled to 90 percent.[229]
The United States Conference of Catholic Bishops has since taken the lead in opposition to the regulations[230] Cardinal Timothy M. Dolan, the archbishop of New York and president of the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops stated that the provision "represents a challenge and a compromise of our religious liberty".[231] Other organizations, such as Planned Parenthood, supported the provision.[232]
According to Humanae Vitae (Of Human Life), an encyclical written by Pope Paul VI and issued on July 25, 1968 by the Roman Catholic Church, contraception is forbidden bynatural law.
Similarly excluded [as lawful] is any action which either before, at the moment of, or after sexual intercourse, is specifically intended to prevent procreation—whether as an end or as a means.[233]
The Agudath Israel of America and the Union of Orthodox Jewish Congregations of America have also opposed the regulations. According to Rabbi Abba Cohen, Agudath Israel's Vice President for Federal Government Affairs, "this mandate, which is binding on all faith-based entities other than a narrowly confined group of religious institutions, offends First Amendment principles."[234]
The regulations issued under the act are also opposed by active Christian Evangelicals.[235]
The Obama administration proposed changes in response to the criticism. Under the proposed new regulation, birth control medication would be provided by the insurers, without direct involvement by the religious organization. The Catholic Health Association (CHA) accepted this compromise. The CEO of the CHA, Carol Keehan, stated, "The framework developed has responded to the issues we identified that needed to be fixed." The vice president of Catholic identity and mission at Mount St. Mary's University, Stuart Swetland, said, "It shows [Obama] and the administration are listening to our concerns", but reserved the right to "examine the details". However, the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops continued to oppose the regulation, saying that the regulation still requires Catholics in the insurance industry to violate their consciences.[232] Catholic opinion is split with a The New York Times/CBS News poll showing 57% support of the regulations among Catholic voters and about the same by non-Catholics.[236]
On March 16, 2012, regulations were issued which ensure coverage for employees of enterprises controlled by religious institutions that self-insure. Regulations were also issued which require coverage for students at institutions controlled by religious organizations which purchase insurance. It is believed by the federal government that it is not possible under current law to require contraceptive coverage for students at institutions controlled by religious organizations which self-insure.[237][238]
[edit]Other effects on individuals
For the effect on health insurance premiums, the CBO referred[183]:15 to its November 2009 analysis[239] and stated that the effects would "probably be quite similar" to that earlier analysis. That analysis forecasted that by 2016, for the non-group market comprising 17% of the market, premiums per person would increase by 10 to 13% but that over half of these insureds would receive subsidies that would decrease the premium paid to "well below" premiums charged under current law. For the small group market, 13% of the market, premiums would be impacted 1 to −3% and −8 to −11% for those receiving subsidies; for the large group market comprising 70% of the market, premiums would be impacted 0 to −3%, with insureds under high premium plans subject to excise taxes being charged −9 to −12%. The analysis was affected by various factors including increased benefits particularly for the nongroup markets, more healthy insureds due to the mandate, administrative efficiencies related to the health exchanges, and insureds under high premium plans reducing benefits in response to the tax.[239]
The Associated Press reported that, as a result of the Act's provisions concerning the Medicare Part D coverage gap, individuals falling in this "donut hole" would save about 40 percent.[240] Almost all of the savings came because, with regard to brand-name drugs, the Act secured a discount from pharmaceutical companies.[240] The change benefited more than two million people, most of them in the middle class.[240]
[edit]Effect on national spending
The United States Department of Health and Human Services reported that the bill would increase "total national health expenditures" by more than $200 billion from 2010 to 2019.[8][241] The report also cautioned that the increases could be larger, because the Medicare cuts in the law may be unrealistic and unsustainable, forcing lawmakers to roll them back. The report projected that Medicare cuts could put nearly 15% of hospitals and other institutional providers into debt, "possibly jeopardizing access" to care for seniors.[242][243]
Surgeon Atul Gawande has noted the bill contains a variety of pilot programs that may have a significant impact on cost and quality over the long-run, although these have not been factored into CBO cost estimates. He stated these pilot programs cover nearly every idea healthcare experts advocate, except malpractice/tort reform. He argued that a trial and error strategy, combined with industry and government partnership, is how the U.S. overcame a similar challenge in the agriculture industry in the early 20th century.[244]
The Business Roundtable, an association of CEOs, commissioned a report from the consulting company Hewitt Associates that found that the legislation "could potentially reduce that trend line by more than $3,000 per employee, to $25,435" with respect to insurance premiums. It also stated that the legislation "could potentially reduce the rate of future health care cost increases by 15% to 20% when fully phased in by 2019". The group cautioned that this is all assuming that the cost-saving government pilot programs both succeed and then are wholly copied by the private market, which is uncertain.[245]
After the bill was signed, AT&T, Caterpillar, Verizon, and John Deere issued financial reports showing large charges against earnings, up to US$1 billion in the case of AT&T, attributing the additional expenses to tax changes in the new health care law.[246] Under the new law, starting in 2013 companies can no longer deduct a subsidy for prescription drug benefits granted under Medicare Part D.[247]
[edit]Political impact
[edit]Public opinion
Polls indicated that a majority of Americans did not support the overall law, although specific elements were very popular across the political spectrum, with the notable exception of the mandate to purchase insurance. Democrats favored the law, while Republicans and Independents did not. For example, a Reuters-Ipsos poll during June 2012 indicated the following:
- 56% of Americans overall were against the law, with 44% supporting it. By party affiliation, 75% of Democrats, 27% Independents, and 14% of Republicans favored the law overall.
- 82% favored banning insurance companies from denying coverage to people with pre-existing conditions.
- 61% favored allowing children to stay on their parents' insurance until age 26.
- 72% supported requiring companies with more than 50 employees to provide insurance for their employees.
- 61% opposed requiring all U.S. residents to own health insurance. By party affiliation, 19% of Republicans, 27% of Independents, and 41% of Democrats favored the mandate that all Americans buy health insurance.[248]
- Other topics receiving majority support among all three affiliations included: creation of insurance pools so small businesses and the uninsured had access to insurance exchanges to take advantage of large group pricing benefits; and providing subsidies on a sliding scale to aid individuals and families who cannot afford health insurance.[249][250]
Other specific ideas that showed majority support, such as purchasing drugs from Canada, limiting malpractice awards, and reducing the age to qualify for Medicare, were not enacted.[251]
Public opinion supported healthcare reform proposals in 2008, but turned negative when the plan changed in 2009, and remains opposed to the final version that was signed in 2010.[252][253] Though in 2008 then-Senators Barack Obama and Joseph Biden campaigned against requiring adults to buy insurance;[254] in 2009 President Obama reportedly changed his mind and agreed with insurance industry and Democratic Congressional proposals to include an individual mandate.[255][256] Public opinion of the legislation turned negative when the individual mandate proposal was announced, and remains opposed by a margin of 10 percentage points.[252][253][257]
In March 2010, pollsters probed the reasons for opposition. In a CNN poll, 62% of respondents said the Act would "increase the amount of money they personally spend on health care," 56% said the bill "gives the government too much involvement in health care," and only 19% said they and their families would be better off with the legislation.[258] In The Wall Street Journal, pollsters Scott Rasmussen and Doug Schoen wrote, "One of the more amazing aspects of the health-care debate is how steady public opinion has remained... 81% of voters say it's likely the plan will end up costing more than projected [and 59%] say that the biggest problem with the health-care system is the cost: They want reform that will bring down the cost of care. For these voters, the notion that you need to spend an additional trillion dollars doesn't make sense."[259] USA Today found opinions were starkly divided by age, with a solid majority of seniors opposing the bill and a solid majority of those younger than 40 in favor.[260]
A June 2012 Reuters-Ipsos poll indicated that much of the opposition to the law was because Americans wanted more reform, not less. About one-third of Republicans and independents who oppose the law did so because it did not go far enough to fix healthcare. 71% of Republican opponents reject it overall, while 29% believed it did not go far enough, while independent opponents are divided 67% to 33%. Among Democratic opponents, 67% reject it overall, and 51% wanted the measure to go further.[248]
In the November 2010 midterm election, Democrats lost more seats in Congress than any party in any midterm in more than 70 years. Politico reported that five House Democrats had run political ads highlighting their "no" votes on the bill, while there had not been any political ads highlighting a "yes" vote since April, when Harry Reid ran one.[261]
As of February 2012, 72% of registered voters believe PPACA's individual mandate is unconstitutional, while only 20% say it is permissible.[262] By a margin of 50% to 39%, Americans say the Supreme Court should overturn the entire statute.[263] The Supreme Court hearings occasioned public demonstrations including prayer vigils coordinated by theWhite House[264] and Tea Party Protests.[265]
[edit]Term "Obamacare"
The term "Obamacare", which has been characterized as pejorative,[266][267][268] continues to be widely used to refer to the legislation, largely by its opponents.[269] Use of the term in a positive sense has been suggested by Democratic politicians such as John Conyers (D-MI).[270] President Obama said subsequently, "I have no problem with people saying Obama cares. I do care."[271] Because of the number of "Obamacare" search engine queries, the Department of Health and Human Services purchased Googleadvertisements, triggered by the term, to direct people to the official HHS site.[269] In March 2012, the Obama reelection campaign embraced the term "Obamacare", urging Obama's supporters to post Twitter messages that begin, "I like #Obamacare because...".[272] According to an analysis by the Sunlight Foundation, the term "Obamacare" has been used nearly 3,000 times since its debut as a phrase on Capitol Hill in July 2009.[3]
According to The New York Times, the term was first put in print in March 2007, when health care lobbyist Jeanne Schulte Scott penned it in a health industry journal. "We will soon see a 'Giuliani-care' and 'Obama-care' to go along with 'McCain-care,' 'Edwards-care,' and a totally revamped and remodeled 'Hillary-care' from the 1990s," Schulte Scott wrote.[3] The word was first uttered in a political campaign by Mitt Romney in May 2007 in Des Moines, Iowa. Romney said: "In my state, I worked on health care for some time.We had half a million people without insurance, and I said, 'How can we get those people insured without raising taxes and without having government take over heath care'. And let me tell you, if we don't do it, the Democrats will. If the Democrats do it, it will be socialized medicine; it'll be government-managed care. It'll be what's known as Hillarycare or Barack Obamacare, or whatever you want to call it."[3]
[edit]Impact on child-only policies
In September 2010, some insurance companies announced that in response to the law, they would end the issuance of new child-only policies.[273][274] Kentucky Insurance Commissioner Sharon Clark said the decision by insurers to stop offering such policies was a violation of state law and ordered insurers to offer an open enrollment period in January 2011 for Kentuckians under 19.[275] An August 2011 Congressional report found that passage of the health care law prompted health insurance carriers to stop selling new child-only health plans in many states. Of the 50 states, 17 reported that there were currently no carriers selling child only health plans to new enrollees. Thirty-nine states indicated at least one insurance carrier exited the child-only market following enactment of the health care laws.[276]
[edit]Constitutional challenges
[edit]Challenges by states
Organizations and lawmakers who opposed the passage of the bill threatened to take legal action against it upon its passage[277] and several court challenges are currently at various stages of development. The target of the threatened lawsuits were several key provisions of the bill. Some claimed that fining individuals for failing to buy insurance is not within the scope of Congress's taxing powers. Idaho legislators passed a law that directed its attorney general to sue if mandatory insurance becomes federal law, which he duly did. A total of 28 states have filed joint or individual lawsuits (including 26 states engaged in a joint action) to overturn the individual mandate portions of the law.[278][279][280][280][281][282][283][284][285] In a press release, the Attorneys General for several states indicated their primary basis for the challenge was a violation of state sovereignty. Their release repeated the claim challenging the federal requirement under threat of penalty, that all citizens and legal residents have qualifying health care coverage. It also claimed that the law puts an unfair financial burden on state governments.[283] The lawsuit states the following legal rationale:
Regulation of non-economic activity under the Commerce Clause is possible only through the Necessary and Proper Clause. The Necessary and Proper Clause confers supplemental authority only when the means adopted to accomplish an enumerated power are 'appropriate', are 'plainly adapted to that end', and are 'consistent with the letter and spirit of the constitution.' Requiring citizen-to-citizen subsidy or redistribution is contrary to the foundational assumptions of the constitutional compact.[286]
Other states were either expected to join the multi-state lawsuit or are considering filing additional independent suits.[281][287][288] Members of several state legislatures are attempting to counteract and prevent elements of the bill within their states. Legislators in 29 states have introduced measures to amend their constitutions to nullify portions of the health care reform law. Thirteen state statutes have been introduced to prohibit portions of the law; two states have already enacted statutory bans. Six legislatures had attempts to enact bans, but the measures were unsuccessful.[289] In August 2010, a ballot initiative passed overwhelmingly in Missouri that would exempt the state from some provisions of the bill. Most legal analysts expect that the measure will be struck down if challenged in Federal court.[290]
[edit]Reactions from legal experts
In February 2011, Alexander Bolton wrote in The Hill that consensus among legal experts largely changed following Judge Roger Vinson's decision in Florida et al v. United States Department of Health and Human Services. He said that prior to the ruling, it was widely felt that the Supreme Court would uphold the law by a comfortable margin, but now legal scholars generally feel it would be a 5–4 decision. Georgetown University Law Center professor Randy Barnett said, "There's been a big change in the conventional wisdom ... the temperature of law professors has changed considerably," and described the Florida decision as "extremely deep in its discussion of principles and constitutional doctrine".[291]
[edit]Federal Court rulings
[edit]U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Florida Ruling
Further information: Florida v. United States Department of Health and Human Services
On January 31, 2011, Judge Roger Vinson in Florida v. United States Department of Health and Human Services declared the law unconstitutional in an action brought by 26 states, on the grounds that the individual mandate to purchase insurance exceeds the authority of Congress to regulate interstate commerce. Vinson further ruled the clause was not severable, which had the effect of striking down the entire law.[292][293]
On August 12, 2011, a divided three-judge panel of the 11th Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed Judge Vinson's decision in part: the court agreed that the mandate was unconstitutional, but held that it could be severed, allowing the rest of the PPACA to remain.[294]
In September 2011, the Department of Justice decided not to ask for an en banc review by the 11th Circuit, and instead asked the U.S. Supreme Court to hear the case.[295][296]On November 14, 2011, the Supreme Court agreed to hear the case, with oral arguments expected in March 2012 and a decision expected by June 2012.[13] However, "Conservative interest groups and Republican lawmakers want Justice Elena Kagan off the health care case. Liberals and Democrats in Congress say it's Justice Clarence Thomaswho should sit out....", though this is considered by many legal and ethical experts to be a questionable approach that is highly unlikely to occur.[297]
According to details of the upcoming proceedings from an online article posted on Monday, December 19, 2011, by Mike Sacks of AOL News Huffington Post Politics, the U.S. Supreme Court will hear oral arguments- an unusually long total of five and a half hours- over three days from Monday, March 26 to Wednesday, March 28, 2012.[298]
[edit]Virginia v. Sebelius
Main article: Virginia v. Sebelius
The first federal court ruling in the legal challenges to the health care act came on August 2, 2010, in response to the suit brought by Virginia's attorney general. U.S. District JudgeHenry E. Hudson denied the Justice Department's request to have the suit dismissed, citing the complex constitutional questions the law raises and writing that the PPACA "radically changes the landscape of health insurance coverage in America."
On December 12, 2010, in the first case rejecting the law's constitutionality, Judge Hudson ruled that the individual mandate was unconstitutional, and that the "tax" imposed on people who choose not to have a "minimum essential coverage plan" was in practice a "penalty" outside the federal government's constitutional authority to raise revenues. Judge Hudson stated he could find no precedent for extending either the Commerce Clause or the General Welfare Clause to encompass regulation of a person's decision not to purchase a product. He ruled the provision to be beyond the power given to Congress under the Commerce Clause. His ruling covered only Section 1501 of the Act, and severed that requirement without discussing the rest of the law.[299][300][301]
A three-judge panel from the 4th Circuit Court of Appeals unanimously ruled on September 8, 2011, that the state did not have the authority to challenge the law, saying "... we vacate the judgment of the district court and remand with instructions to dismiss the case for lack of subject-matter jurisdiction."[302] The state's attorney general said they planned to appeal the decision.
[edit]U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Ruling
In Seven-Sky v. Holder, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia ruled that the law is Constitutional.[303][304] The Constitutional Accountability Center remarked that this court consists of many conservative judges and they found the law constitutional.[304] Specifically, Senior Judge Lawrence Silberman, well known in conservative circles as a conservative intellectual, and who ruled that the District of Columbia's handgun law was unconstitutional, ruled that the law is constitutional. Silberman said "the right to be free from federal regulation is not absolute and yields to the imperative that Congress be free to forge national solutions to national problems".[303]
[edit]U.S. District Court for the Western District of Virginia Ruling
On November 30, 2010, U.S. District Court Judge Norman K. Moon, who sits in Virginia, also declared the individual mandate constitutional in Liberty University v. Geithner. He also declared the employer mandate constitutional. He rejected two other arguments that government lawyers have made in cases across the country in defending the new law: first, that no one has legal standing to bring challenges at this point to the 2014 mandates, and second that any such challenge is premature. He rejected the challengers' basic argument that Congress had no authority to order someone to give up their own desire not to buy a commercial product and force them into a market they do not want to enter. He said:
Regardless of whether one relies on an insurance policy, one's savings, or the backstop of free or reduced-cost emergency room services, one has made a choice regarding the method of payment for the health care services one expects to receive. Far from "inactivity", by choosing to forgo insurance, [individuals] are making an economic decision to try to pay for health care services later, out of pocket, rather than now, through the purchase of insurance ... As Congress found, the total incidence of these economic decisions has a substantial impact on the national market for health care by collectively shifting billions of dollars on to other market participants and driving up the prices of insurance policies.[305]
[edit]U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia Ruling
On February 22, 2011, Judge Gladys Kessler of the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia, rejected a challenge to the law in Mead v. Holder by five individuals who argued, among other things, that the Affordable Care Act violated the Religious Freedom Restoration Act, and that the individual mandate exceeded Congress's power under the Interstate Commerce Clause. Kessler rejected as "pure semantics" plaintiffs' argument that failing to acquire insurance was the regulation of inactivity, noting that "those who choose not to purchase health insurance will ultimately get a 'free ride' on the backs of those Americans who have made responsible choices to provide for the illness we all must face at some point in our lives." Kessler ruled that individual mandate was a valid exercise of Congress's power to regulate interstate commerce.[306][307]
[edit]U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Michigan Ruling
On October 8, 2010, U.S. District Court Judge George Caram Steeh in Thomas More Law Center v. Obama wrote that in his view the PPACA, including the individual mandate, was constitutional.[308] He rejected a private suit[309] filed by Michigan's Thomas More Law Center and several state residents that focused on the Commerce Clause, deciding that Congress had the power to pass the law because it affected interstate commerce and was part of a broader regulatory scheme.[310][311]
On June 29, 2011, a divided three-judge panel of the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed the decision.[312] Judge Jeffrey Sutton, a member of the three judge panel appointed by George W. Bush, was the first Republican-appointed judge to rule that the law is constitutional.[313]
[edit]U.S. Supreme Court
On November 14, 2011, the Supreme Court of the United States issued a writ of certiorari to the United States Appeals Court for the Eleventh Circuit to consider appeals to its rulings in National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius and Florida v. United States Department of Health and Human Services. Briefings were filed over the next four months. On March 26, 2012, the court began hearing oral arguments regarding four questions.[314][315][316]
[edit]Anti-Injunction Act question
[Is] the suit brought by [the state Attorneys General] to challenge the minimum coverage provision of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act barred by the Anti-Injunction Act?
Starting at 10:00 a.m. ET on March 26, 2012, Robert A. Long, a court appointed amicus, had 40 minutes to argue that the Anti-Injunction Act precludes the challenge. The Solicitor General of the United States had 30 minutes to argue that Anti-Injunction Act does not apply. The state Attorneys General had 20 minutes to argue that Anti-Injunction Act does not apply.[317]
[edit]Minimum Coverage Provision question
[Did Congress have] the power under Article I of the Constitution to enact the minimum coverage provision?
Starting at 10:00 a.m. ET on March 27, the Solicitor General had 60 minutes to argue that the minimum coverage provision is constitutional. The state Attorneys General and the council for the National Federation of Independent Business each had 30 minutes to argue that the provision is unconstitutional.[318]
[edit]Severability question
Must PPACA be invalidated in its entirety because it is non-severable from the individual mandate that exceeds Congress' limited and enumerated powers under the Constitution?
Starting at 10:00 a.m. ET on March 28, the state Attorneys General had 30 minutes to argue that the entire law must be invalidated. The Solicitor General had 30 minutes to argue that only the guaranteed issue and community rating provisions are inseverable from the minimum coverage provision. H. Bartow Farr argued that the minimum coverage provision is completely severable from the rest of the act.[319][320]
[edit]Federalism and Medicaid question
Does Congress exceed its enumerated powers and violate basic principles of federalism when it coerces States into accepting onerous conditions that it could not impose directly by threatening to withhold all federal funding under the single largest grant-in-aid program Medicaid?
Starting at 2:00 p.m. ET on March 28, the state Attorneys General had 30 minutes to argue that withholding funds violates federalism. The Solicitor General had 30 minutes to argue that it does not.[321]
[edit]Arguments and commentary
The March 26th to 28th Supreme Court hearings focused on the four questions above, in consideration of an appeal to lower court rulings on healthcare lawsuits filed by 26 state attorneys general and the National Federation of Independent Business. The original suits aimed to challenge the "individual mandate" provision, requiring all individuals to purchase insurance or pay a penalty. The plaintiffs argue that forcing individuals to buy a product is unconstitutional as Congress may only regulate economic activity not require it. The Obama administration argues that the mandate regulates how and whether individuals pay for the healthcare they receive.[322]
The first day of Supreme Court arguments on March 26, 2012, concerned the Anti-Injunction Act and whether this should prevent the court from hearing the challenge to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, until the plaintiffs had either purchased the insurance or paid the penalty for not doing so.
On March 27, the court heard arguments for and against the "individual mandate", intended to spread costs by requiring all Americans to purchase health insurance or pay a penalty.[323] Conservative justices raised critical questions about the constitutionality of the government forcing individuals to purchase insurance.[324] In particular, JusticesAntonin Scalia and John Roberts questioned whether allowing the government to mandate this purchase would allow other mandates in future.[325] The Washington Post reported that while statements by Justice Anthony M. Kennedy were interpreted by advocates for both sides as a sign he would rule in their favor, by the end of the day the consensus emerged that the odds were in favor of some or all of the Act being overturned.[323]
The third day of hearings involved consideration of whether the rest of the Act would survive if the individual mandate was ruled unconstitutional.[326][324] According to theAssociated Press, the justices seemed to have agreed that there were at least two key changes to insurance as part of the Act that could not survive without the individual mandate: the requirement for insurance companies to provide coverage regardless of pre-existing medical conditions and limits on the premiums that companies can charge based on age or health.[327] On the final day the justices also considered whether the federal government had coerced states into agreeing to the expansion of Medicaid under the Act.[328] The counsel on behalf of the states argued that the provision of the Act that covers the expansion is unconstitutional, as it uses the risk of losing Medicaid funding to coerce the states to expand their Medicaid rolls, thereby violating the principles of federalism.[329] The states' argument appeared to be taken seriously by conservative justices, according to The Washington Post, however the justices were split ideologically on the issue.[330]
On April 2, 2012 Obama said, "I'm confident that the Supreme Court will not take what would be an unprecedented, extraordinary step of overturning a law that was passed by a strong majority of a democratically elected Congress." The following day, a three-judge panel for the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals ordered the U.S. Justice Department to explain by April 5 whether the administration believes judges have the power to strike down a federal law. The reply of Justice Department attorney Dana Lydia Kaersvang was "yes."[331][332][333]
[edit]Ruling in National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius
Main article: National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius
[edit]Majority opinion
On June 28, 2012, the Supreme Court voted 5–4 to uphold most aspects of the law. In Chief Justice John Roberts' words:
The Affordable Care Act's requirement that certain individuals pay a financial penalty for not obtaining health insurance may reasonably be characterized as a tax. Because the Constitution permits such a tax, it is not our role to forbid it, or to pass upon its wisdom or fairness.[14]
The critical distinction that the majority found convincing was that the Act merely imposed a relatively small tax upon the choice to not buy health insurance, but it did not make that choice itself a crime per se. Although the Court has seen cases in the past in which Congress tried to evade limitations on other enumerated powers through inappropriate interpretations of the Taxing Clause, the Court ruled that the Act clearly fell within the boundaries outlined in those cases.
The Court also rejected arguments that the statute's treatment of individuals who fail or refuse to purchase health insurance was unconstitutional (the "inactivity" arguments). The Court distinguished the power to regulate interstate commerce from the power to impose a tax, stating:
-
- ....it is abundantly clear the Constitution does not guarantee that individuals may avoid taxation through inactivity. A capitation, after all, is a tax that everyone must pay simply for existing, and capitations are expressly contemplated by the Constitution. The Court today holds that our Constitution protects us from federal regulation under the Commerce Clause so long as we abstain from the regulated activity. But from its creation, the Constitution has made no such promise with respect to taxes.[334]
[edit]Dissenting opinions
The dissenting justices in National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius argued that:
The Court today decides to save a statute Congress did not write. It rules that what the statute declares to be a requirement with a penalty is instead an option subject to a tax. And it changes the intentionally coercive sanction of a total cut-off of Medicaid funds to a supposedly noncoercive cut-off of only the incremental funds that the Act makes available.[15]
[edit]Key case questions and answers
In its ruling[335][336] the Supreme Court answered several key questions with U.S. health care law. CNN summarizes the questions and answers as follows:[337]
1. Question: Can the court decide the constitutionality of health care now, or does it have to wait a few years? (To answer, the court had to decide whether a penalty the law imposes on people who do not have health insurance amounts to a tax. A previously obscure law mandated that the legality of a tax cannot be challenged until it is imposed, and the health care law doesn't call for penalties until 2014.) The court's answer: The court upheld the entire law.
2. Question: Is the requirement that people have health insurance - the so-called individual mandate - constitutional? The court's answer: Chief Justice John Roberts wrote that the commerce clause did not apply, but the mandate stands under the taxing clause.
3. Question: If the individual mandate is unconstitutional, can the rest of the law stand, or is the whole thing unconstitutional? The court's answer: The mandate is constitutional, rendering moot further questions on the rest of the law.
4. Question: Can the federal government force states to expand their share of Medicaid costs and administration? The court's answer: Yes, but the justices ruled that the federal government cannot remove existing Medicaid funding if the states choose not to participate in the new program.
[edit]Repeal efforts
[edit]111th Congress
Reps. Steve King of Iowa and Michele Bachmann of Minnesota, both Republicans, introduced bills in the House to repeal the Act shortly after it was passed, as did Sen. Jim DeMint in the Senate.[338] None of the three bills were considered by either body.
[edit]112th Congress
In 2011, the Republican-controlled House of Representatives voted 245–189 to approve a bill entitled "Repealing the Job-Killing Health Care Law Act" (H.R.2),[339] which, if enacted, would repeal the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the health care-related text of the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010. All Republicans and 3 Democrats voted for repeal.[340] In the Senate, the bill was offered as an amendment to an unrelated bill, and was subsequently voted down.[341] Before votes in both houses of the Congress took place, President Obama stated that he would veto the bill should it pass both chambers.[342] Democrats in the House proposed that repeal not take effect until a majority of the Senators and Representatives had opted out of the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program. The Republicans voted down this measure.[343]
On June 28, 2012, following the law being ruled as constitutional by the Supreme Court, Eric Cantor stated that the House would again vote to repeal the law on July 11 when Congress returns from recess.[344][345][346]
[edit]Job consequences of repeal
A spokesman for Republican Majority Leader Eric Cantor stated, "This is a job-killing law, period. Anyone who argues otherwise is ignoring the construct of the health care law and the widely accepted facts."[347] The House Republican leadership justified its use of the term "job killing" by contending that the PPACA would lead to a loss of 650,000 jobs, and attributing that figure to a report by the Congressional Budget Office.[347] However, the CBO report specifically stated that the negative effect on jobs was because people would voluntarily choose to work less once they have health insurance outside of their jobs.[348] FactCheck noted that the 650,000 figure was not in the CBO report, and said that the Republican statement "badly misrepresents what the Congressional Budget Office has said about the law. In fact, CBO is among those saying the effect 'will probably be small.'"[347] The Republicans also cited a study by the National Federation of Independent Business, but PolitiFact.com said that the 2009 NFIB study had concerned an earlier version of the bill that differed significantly from what was enacted.[349] PolitiFact rated the Republican statement as False.[349]
[edit]Effect of repeal proposals on federal budget projections
The CBO estimated that repealing the entire PPACA (including both its taxing and spending provisions) would increase the net 2011-2021 federal deficit projections by $210 billion.[213] Others disagree, arguing that estimate was based on unrealistic assumptions; House Speaker John Boehner said, "I don't think anyone in this town believes that repealing Obamacare is going to increase the deficit."[350] In May 2011, CBO analyzed proposals to prevent the use of appropriated funds to implement the legislation, and wrote that "a temporary prohibition, extending through the remainder of fiscal year 2011, would reduce the budget deficit by about $1.4 billion in 2011 but would increase deficits by almost $6 billion over the 2011-2021 period... CBO cannot determine whether changes in spending under a permanent prohibition would produce net costs or net savings relative to its baseline projection, which assumes full implementation."[351]
[edit]Temporary waivers
Interim regulations have been put in place for a specific type of employer funded insurance, the so-called "mini-med" or limited benefit plans, which are low-cost to employers who buy them for their employees, but cap coverage at a very low level. Such plans are sometimes offered to low-paid and part-time workers, for example in fast food restaurants or purchased direct from an insurer. Most company-provided health insurance policies starting on or after September 23, 2010 and before September 23, 2011 may not set an annual coverage cap lower than $750,000,[352] a lower limit that is raised in stages until 2014, by which time no insurance caps are allowed at all. By 2014, no health insurance, whether sold in the individual or group market, will be allowed to place an annual cap on coverage. The waivers have been put in place to encourage employers and insurers offering mini-med plans not to withdraw medical coverage before the full regulations come into force (by which time small employers and individuals will be able to buy non-capped coverage through the exchanges) and are granted only if the employer can show that complying with the limit would mean a significant decrease in employees' benefits coverage or a significant increase in employees' premiums.[352]
Among those receiving waivers were employers, large insurers, such as Aetna and Cigna, and union plans covering about one million employees. McDonald's, one of the employers that received a waiver, has 30,000 hourly employees whose plans have annual caps of $10,000. The waivers are issued for one year and can be reapplied for.[353][354]Referring to the adjustments as "a balancing act", Nancy-Ann DeParle, director of the Office of Health Reform at the White House, said, "The president wants to have a smooth glide path to 2014."[353] On January 26, 2011, HHS said it had to date granted a total of 733 waivers for 2011, covering 2.1 million people, or about 1% of the privately insured population.[355] In June 2011, the Obama Administration announced that all applications for new waivers and renewals of existing ones have to be filed by September 22 of that year, and no new waivers would be approved after this date.[356]
[edit]See also
- Comparison of Canadian and American health care systems
- Universal health care
- U.S. health care compared with 8 other countries in tabular form
- Clinton health care plan of 1993
- Massachusetts health care reform law ("Romneycare"), which served as a model for the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act[357]
[edit]
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obamacare
*
... the U.S. Supreme Court passed this today 5-4 ... !
*
World University and School's beginning Medical School is excited to explore some of these possibilities in this Act for online care ...
http://worlduniversity.wikia.com/wiki/World_University_Medical_School
*
We the people seem to have just gotten universal health care :)
...




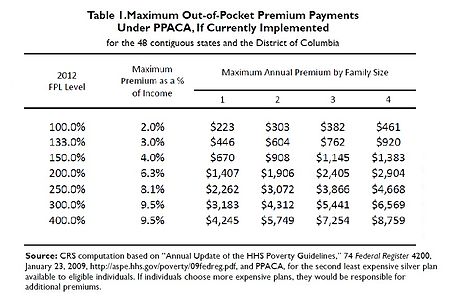



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.